Semiconductors Explained: What They Are, How They’re Made, and Their Types – The Core of Modern Technology
Semiconductors are at the heart of modern technology. They power your smartphones, laptops, and even electric cars. Understanding what they are, how they’re made, and what they do can give us a clear insight into the digital world we live in today. This news was last updated on[insert date], providing you with the latest information.
What is a Semiconductor?
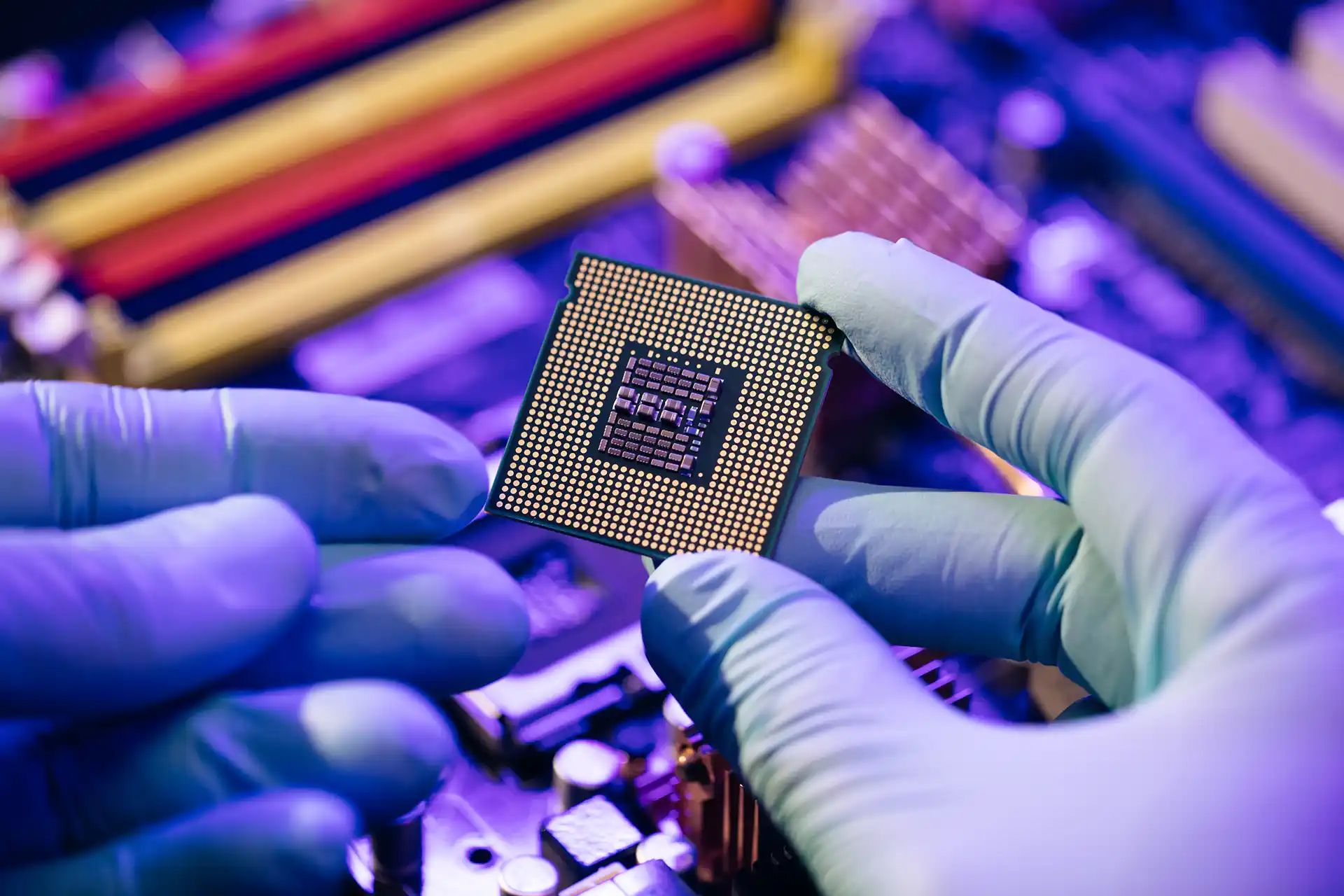
Asemiconductoris a material that can conduct electricity, but not as well as metals like copper or silver. It stands between a conductor (like metal) and an insulator (like rubber). The unique thing about semiconductors is that their conductivity can be controlled. This makes them ideal for use in electronic devices.
The most common semiconductor material issilicon. It’s found everywhere on Earth, making it an affordable and accessible option. Other materials likegermaniumandgallium arsenideare also used, but silicon is the most popular due to its properties and availability.
How are Semiconductors Made?
The process of making a semiconductor is highly complex. It starts withsiliconbeing extracted from sand. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how a semiconductor is made:
- Extracting Silicon: Silicon is taken from sand and purified. Silicon dioxide (SiO2) is removed, leaving behind pure silicon.
- Creating Silicon Wafers: The purified silicon is melted and then shaped into a large cylinder called aningot. This ingot is sliced into very thin disks calledwafers. These wafers become the base of the semiconductor.
- Adding Impurities (Doping): To control how the semiconductor behaves, small amounts of other materials (like phosphorus or boron) are added to the silicon wafer. This process is calleddoping. It changes the wafer’s electrical properties, making it either more positive or more negative.
- Etching Circuits: Microscopic circuits are etched onto the wafer using chemicals or lasers. These circuits will later help the semiconductor control the flow of electricity.
- Packaging: Once the semiconductor is ready, it’s cut into smaller pieces and packaged for use in electronic devices like smartphones, computers, and more.
How Many Types of Semiconductors Are There?
Semiconductors can be classified intotwo main typesbased on their electrical properties:
1.Intrinsic Semiconductors
Anintrinsic semiconductoris made of pure materials, like pure silicon. There are no impurities in it, and its ability to conduct electricity is limited. These types of semiconductors conduct electricity only when they are exposed to heat or light. In other words, their conductivity depends on external conditions.
2.Extrinsic Semiconductors
Anextrinsic semiconductorhas been doped with impurities to change its conductivity. This type is more commonly used in electronics because it offers better control. Extrinsic semiconductors are further divided into:
- N-type Semiconductors: These are doped with materials like phosphorus, which have more electrons than silicon. This creates more negative charge carriers (electrons), allowing current to flow easily.
- P-type Semiconductors: These are doped with materials like boron, which have fewer electrons than silicon. This creates “holes” (spaces where electrons can move), and these holes act as positive charge carriers.
BothN-typeandP-typesemiconductors are essential in creating the components used in electronic devices, such asdiodes,transistors, andintegrated circuits (ICs).
What Does a Semiconductor Do?
Semiconductors play a key role in controlling the flow of electricity in electronic devices. They can switch on and off the flow of current, amplify signals, and manage electrical power. Here’s a closer look at their functions:
1.Switching
One of the primary roles of a semiconductor is to act as aswitch. For example, in a computer, semiconductors control when electricity should flow and when it should stop. This ability allows computers to perform calculations and process information at lightning speed.
2.Amplification
Semiconductors can also be used toamplify signals. In a smartphone, for instance, semiconductors help to amplify your voice during a call so that the person on the other end can hear you clearly.
3.Energy Conversion
Semiconductors are also found in devices thatconvert energy. For example, in solar panels, semiconductors help convert sunlight into electricity. This is called thephotovoltaic effect.
Why Are Semiconductors So Important?
Without semiconductors, modern technology would not exist. Here are a few reasons why they are so important:
- They Power Everyday Devices: Semiconductors are used in almost every electronic device you use daily, from mobile phones to kitchen appliances.
- They Enable Advanced Technologies: Innovations likeartificial intelligence (AI),5G networks, andself-driving carsall rely on advanced semiconductors.
- They Improve Efficiency: Modern semiconductors make electronic devices faster and more energy-efficient. They allow for miniaturization, meaning devices can be made smaller and more powerful.
Challenges in Semiconductor Manufacturing
While semiconductors are vital, making them comes with several challenges:
- Precision: The manufacturing process requires a high level of precision. Even the tiniest error in doping or etching can lead to malfunctioning devices.
- Cost: Setting up a semiconductor manufacturing facility is incredibly expensive. It requires specialized equipment and a clean environment to prevent contamination.
- Global Shortages: Recently, there have beensemiconductor shortagesdue to increased demand and supply chain disruptions. This has impacted industries likeautomotive,electronics, andtelecommunications.
The Future of Semiconductors
The demand for semiconductors is expected to grow even more in the coming years. As technologies likeartificial intelligence (AI),quantum computing, andInternet of Things (IoT)expand, so does the need for more efficient and powerful semiconductors.
Innovations like3D semiconductors, where multiple layers of circuits are stacked, are being developed to meet future demands. Additionally, researchers are looking into using new materials, such asgraphene, to create even faster and more energy-efficient semiconductors.
In summary, semiconductors are the foundation of modern electronics. They are materials that control the flow of electricity, making them essential for all kinds of electronic devices. With the ability to switch, amplify, and convert energy, semiconductors are key to powering the digital world. Understanding how they’re made, their types, and their functions can help us appreciate the role they play in the technology we use every day.
Whether you’re using your smartphone, computer, or driving an electric car, semiconductors are behind it all. As technology evolves, semiconductors will continue to be at the forefront, shaping the future of innovation.
NO: 1 Hindi News Website TalkAaj.com (Baat Aaj Ki)
(Read the Latest News of the Country and the World first on TalkAaj (Talk Today), follow us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and Youtube)